Opening Times: Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline Solar Panels: An In-Depth Comparative Analysis
Date:- 06-05-2025 By Admin
As the global transition towards renewable energy accelerates, selecting the appropriate solar panel technology becomes pivotal for maximizing efficiency and return on investment. This comprehensive guide delves into the critical distinctions between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, providing insights to inform your decision-making process.
Understanding Solar Panel Technologies
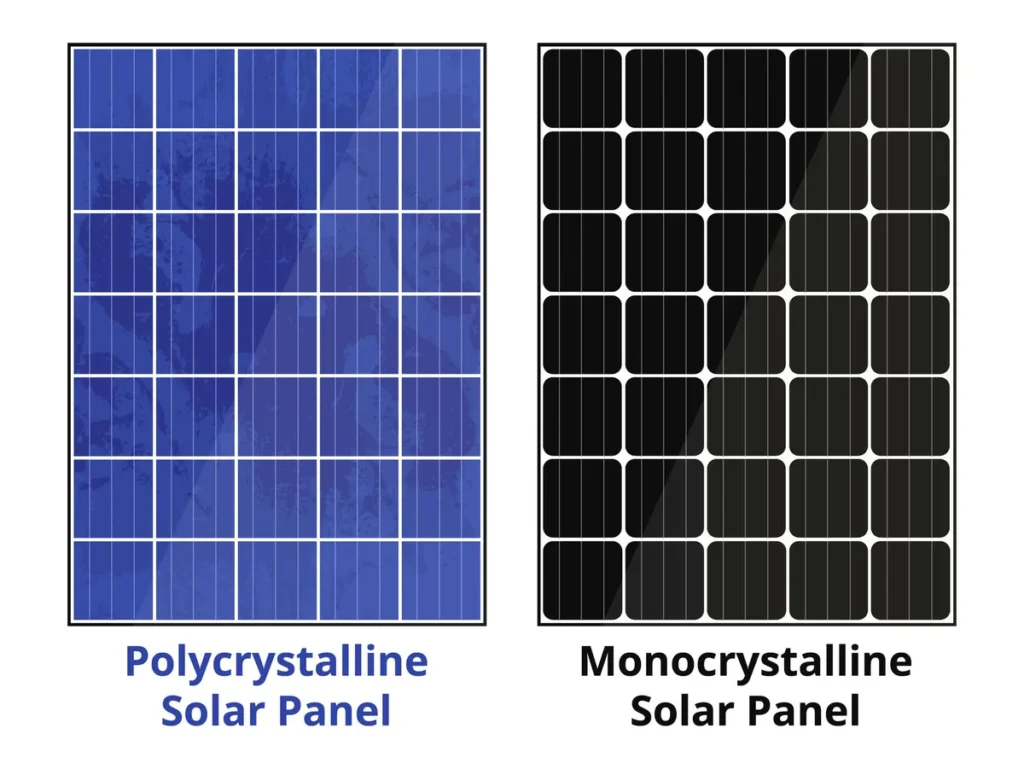
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline panels are fabricated from a single, continuous crystal structure, typically silicon, resulting in a uniform black appearance. This manufacturing process yields high-efficiency panels that perform exceptionally well in various conditions.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline panels consist of multiple silicon crystals melted together, giving them a characteristic blue, speckled look. The production process is less energy-intensive, making these panels more cost-effective but slightly less efficient.
Comparative Analysis: Key Factors
1. Efficiency
-
Monocrystalline Panels: Exhibit higher efficiency rates, typically ranging from 17% to 22%, due to the purity of silicon used.
-
Polycrystalline Panels: Offer efficiency rates between 13% and 17%, attributed to the presence of multiple silicon crystals.
2. Cost Implications
-
Monocrystalline Panels: Generally more expensive, with costs ranging from $1 to $1.50 per watt, due to the complex manufacturing process.
-
Polycrystalline Panels: More affordable, typically costing between $0.90 to $1.00 per watt, owing to simpler production methods.
3. Performance in Low-Light Conditions
-
Monocrystalline Panels: Superior performance in low-light environments, making them suitable for areas with less sunlight.
-
Polycrystalline Panels: Slightly less effective in low-light conditions compared to monocrystalline counterparts.
4. Lifespan and Durability
-
Monocrystalline Panels: Offer a longer lifespan, often exceeding 25 years, with many manufacturers providing warranties up to 30 years.
-
Polycrystalline Panels: Typically have a lifespan of 20 to 25 years, with warranties reflecting this duration.
5. Aesthetic Considerations
-
Monocrystalline Panels: Feature a sleek, black design that blends seamlessly with most rooftops, offering a modern aesthetic.
-
Polycrystalline Panels: Display a blue, speckled appearance, which may be less visually appealing to some homeowners.
Environmental Impact
Manufacturing Process
-
Monocrystalline Panels: Require more energy-intensive manufacturing, leading to a higher initial environmental footprint.
-
Polycrystalline Panels: Utilize a less energy-consuming production process, resulting in a lower environmental impact during manufacturing.
End-of-Life Considerations
Both panel types are recyclable, but the recycling infrastructure and processes are still developing globally. Proper disposal and recycling are essential to minimize environmental harm.
Suitability Based on Installation Scenarios
| Scenario | Recommended Panel Type | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Roof Space | Monocrystalline | Higher efficiency yields more power in confined areas. |
| Budget-Constrained Projects | Polycrystalline | Lower upfront costs make them economically viable. |
| Aesthetic Priority | Monocrystalline | Sleek design enhances visual appeal of installations. |
| High-Temperature Environments | Polycrystalline | Better performance in higher temperatures. |
| Areas with Frequent Cloud Cover | Monocrystalline | Superior low-light performance ensures consistent output. |
Selecting between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels hinges on specific project requirements, including budget, space constraints, aesthetic preferences, and environmental conditions. Monocrystalline panels offer higher efficiency and a longer lifespan, making them suitable for installations where space and performance are paramount. Conversely, polycrystalline panels provide a cost-effective solution with respectable efficiency, ideal for projects with budget limitations.
2026 99Sunfotech Power Pvt Ltd - All Rights Reserved Developed By : Uinfotechnology Pvt. Ltd.

